
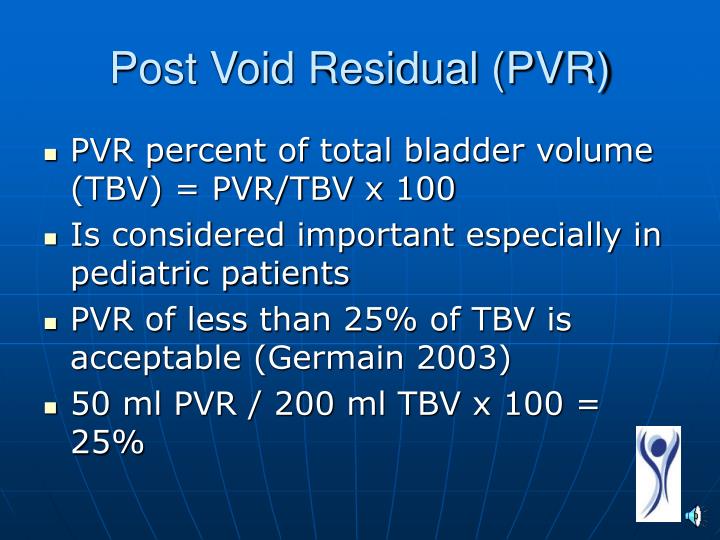
It's normal for the bladder to not completely empty itself. Post-void Residual (PVR)Ī post-void residual (PVR) determines how much urine is left behind after you urinate. Your doctor may also perform a rectal exam to check the strength of these muscles, which can weaken with age or childbirth. During the exam, your doctor may ask you to push down or cough to see how much urine you leak. Your doctor will ask for your health history and perform a pelvic exam.
Excessive fluid intake: A recommended amount of fluid for bladder health can be anywhere from 30-60 ounces per day depending on the individual.Bladder irritants: The most common are caffeine, decaffeinated coffee, carbonated beverages and spicy foods.Urinary tract infections (UTIs), medications and lifestyle behaviors may also contribute to your incontinence. Some women have worsening symptoms around the time of menopause. Aging/MenopauseĪs women age they're more likely to develop urinary incontinence. This is one of the most common causes of urinary incontinence among women. Most women recover, but if you still have urinary incontinence six months after delivery, make an appointment with your doctor. Mixed incontinence is a combination of stress and urge incontinence.The bladder muscle tightens or contracts involuntarily when it should be relaxed. Urge incontinence is usually the result of problems with the bladder muscle.If these structures fail, then the urethra moves too much, leading to incontinence. A condition called intrinsic sphincter deficiency (ISD) can result from damage to the urethra and the urethral sphincters. This condition usually results in severe stress incontinence. Stress incontinence is a result of damage to the urethra or the bladder neck.Sometimes women experience problems with urination due to other conditions such as frequent bathroom trips or excessive fluid intake.ĭifferent causes contribute to the various forms of incontinence. Mixed incontinence: Women with urinary incontinence generally have stress, urge, and often times mixed incontinence, which is a combination of both stress and urge.The bladder is unable to do its job properly, and urine leaks due to overflow. With this condition the bladder does not empty completely, and as a result the bladder becomes progressively swollen. Overflow: This is a rare condition where women leak small amounts of urine frequently because their bladder is constantly full.Women may experience getting up frequently during the night to urinate, bed-wetting or going to the bathroom every two hours. Urge incontinence or latch key incontinence (over-active bladder): Women with this are not able to wait until it's convenient to empty their bladder because of their weakened ability to tell the bladder to wait.The external force pushes on your bladder and causes urine past the urethra. Stress incontinence: This happens when something you do, such as coughing, laughing, sneezing, jumping, lifting or exercise.Women with urinary incontinence problems may have one or more of the following: Many women experience it when they go for a walk or a run, and they often find it embarrassing and debilitating. Urinary incontinence is often the result of pelvic floor damage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
